Alternative fuels
Clean energy for constructing tomorrow’s sustainable infrastructures
The graph data processed by ISPRA shows how (GHG) Greenhouse Gas emissions have reduced progressively in Italy in recent decades, following a trend that, if sustained by decarbonisation policies, could result in an overall reduction in the future of about 25% by 2040 (compared to 2022 levels).
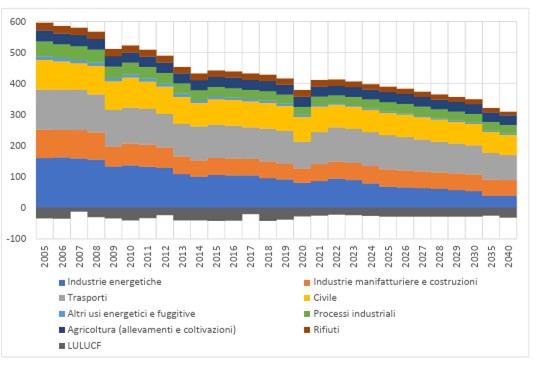
Green house gas emissions by sector [MtCO2e], historically and reference scenario. Sources ISPRA and PNIEC 2024
The graph data processed by ISPRA shows how (GHG) Greenhouse Gas emissions have reduced progressively in Italy in recent decades, following a trend that, if sustained by decarbonisation policies, could result in an overall reduction in the future of about 25% by 2040 (compared to 2022 levels).
To date the transport sector has accounted for a significant portion of overall emissions, amounting to about 26% of the total, and is still one of the most complex sectors to be decarbonised, due to various widely-ranging, complex factors. In the transport sector, and especially the rail segment, emission reduction can take place along integrated, synergic lines, including:
- Promoting a shift to sustainable transport systems worldwide, such as from road to rail.
- Electrifying the various systems using electricity from renewable sources.
- Using alternative, non-fossil fuels.
- Adopting Best Management Practices for sustainability during other life-cycle phases of the transport service, such as when planning and constructing infrastructures.
Infrastructural shortcomings, especially in some areas of the country, make reducing emissions even more wide-ranging and strictly connected to the construction and manufacturing sectors. Within this setting, Italferr stands out as a reference engineering company that promotes an approach to planning and constructing complex infrastructures that includes both sustainability and innovation. The Company makes a significant contribution, along with other companies in the Gruppo Ferrovie dello Stato, by applying its experience to pursuing the Gruppo FS decarbonisation goals, as well as those set at a national and a European level.
As indicated previously, in pursuing decarbonisation, a real contribution can be made by using alternative fuels such as (LCF) low carbon fuels, especially biofuels of biogenic origin. These provide a versatile solution that complements direct electrification, and can be applied to the various sectors with a high environmental impact. It is by no mere chance that bio-refineries in the Country have already started producing such fuels for aviation, demonstrating their adaptability, while the agricultural sector is making an ever more significant contribution to creating circular systems.
While planning infrastructural works, Italferr uses advanced methodologies to evaluate the benefits of using low carbon content fuels in the construction phase. In fact, using them significantly reduces the climatic footprint of worksites and transporting materials, contributing to reducing what is termed the infrastructure’s Embodied Carbon. In terms of alternative low carbon content fuels, the Company also takes part in European research projects, such as the MOST H2 project, analysing the sustainability of innovative solutions and sharing their know-how at an international level.
Carbon footprint evaluations for lot 2 of Doubling of the Decimomannu - Villamassargia Railway Line
The analysis examined the use of HVO (Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil), a fuel produced from spent oils and agroalimentary residue, that can be used in place of traditional diesel for transporting materials and work on site.
The calculation of climate changing emissions associated with the project was audited by an outside body in terms of the principles laid down in UNI EN ISO 14064-1 as part of the annual updating of Italferr’s CO₂ Tariffing Schedule, thereby ensuring the transparency and sturdiness of the results achieved.
The results
By applying Italferr’s methodology to lot 2 of the Doubling of the Decimomannu–Villamassargia railway line it was estimated that, in conventional construction scenarios, total emissions would stand at about 44,000 tCO₂e for the materials, transportation and works classes. This value was taken as a baseline for subsequent evaluations, including the hypothesis of using HVO for transportation and site works.
In order to analyse the consequences of using HVO type fuels, we quantified the emissions associated with transportation and site works, distinguishing the following cases:
- Conventional scenario using fossil diesel: the emissions were calculated using the estimated consumption levels and conventional hypotheses based on the CO2 Tariffing Schedule
- Alternative scenario, using HVO: using only (pure) HVO with average consumption of vehicles increased by 2% and emission factors taken from the DEFRA database (DEFRA Greenhouse gas reporting: conversion factors 2024)
In their turn, the results derived from using HVO can be interpreted via various scenarios, such as:
- Aggregate precautionary scenario, without out separating calculation of the various GHGs: reduction in total project emissions of about 3% compared to the conventional scenario
- “CO₂ Net Zero” scenario, with biogenic, anthropogenic CO2 deemed to be out of scope: reduction of about 23% of total CO2e compared to the conventional scenario
The benefits are particularly marked when concentrating the analysis on only the transportation and site works classes, with a reduction in CO2e of about 82% in evaluations of the CO2 Net Zero scenario.
These numbers confirm that fuel choices for the construction phase can have a significant impact on the carbon footprint of an infrastructural project. The use of low carbon content fuels, especially is combined with other good practices, can therefore provide a real solution on the way to decarbonisation and, more generally, towards an integrated, holistic sustainability model.
In addition the benefits, studied further in Italferr’s evaluations, do not stop at simply reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but also extend to:
- Reducing other pollutants, such as (PM) particles, (CO) carbon monoxide, (NOx) nitrous oxides, heavy metals, etc
- Reduction in exploitation of resources
- Noise reduction
- Waste reduction
Communicating sustainability: Italferr’s commitment to informing on sustainability questions
By studies like this and their contribution to European research projects, Italferr consolidates its approach to responsible planing, in which environmental sustainability is an integral part of decisions from the preliminary phases. At the same time the Company acknowledges the importance of communication and transparency, which are key elements of disseminating knowledge and raising awareness of the impacts and benefits of planning and construction choices.
Evaluating the benefits of alternative fuels does not only provide technical support in decision-making, but is also a way of sharing useful, accessible information, contributing to directing public debate and sector strategies towards more sustainable solutions. By means of this approach, Italferr enhances its contribution to attaining the Gruppo FS Italiane goals, as well as the goals set at a national and European level, in line with the SDG (Sustainable Development Goals).